Power supplies form an integral part of the electro-mechanical world. From a broad perspective, their primary function is to provide electric energy to all types of electronic circuits (e.g. small electronic devices, large machinery) in both the commercial and industrial worlds. From a narrower perspective, their primary function is to power electrical circuits by converting or adapting one form of electrical power into another. Read More…
TDK-Lambda Americas designs and manufactures a wide range of AC-DC and DC-DC power supplies and EMI Filters for Medical, Telecom, Industrial, Datacom, and Test & Measurement applications worldwide. The company has been a major provider of power solutions since 1948. TDK-Lambda is a subsidiary of the TDK Corporation, a leading global electronics company.

Our company offers a variety of standard and custom power supplies. These items are great for a wide range of applications. If you have any special requests then please let our representatives know. If you ever run into any questions or issues then our engineers are available to assist you. There is no project too challenging for our teams! Give us a call today!

For 4 decades, Acopian Power Supplies has specialized in long lasting power supplies (0 volts – 30000 V). We offer AC power supplies, DC power supplies, AC to DC converters, uninterruptible power supply (UPS), AC to DC power supplies & high voltage power supplies. With quality customer service & technical support, we have thousands of power supplies for thousands of applications.
APS are specialists in power conversion and the manufacture of high performance power systems. Products include power converters and inverters; motor drives and brakes; battery chargers; AC and DC power supplies; driver circuits and more. Custom and standard power systems are available.
At Quail Electronics, we are your power cord specialists. Our power supplies consist of green dot cords, high voltage cords, North American and international cords, specialty cords, plus adapters, plugs and strips.

More Power Supply Manufacturers
Understanding the dual meanings of the term “power supply” is essential to clear up the confusion that often surrounds this topic. Broadly defined, almost every electronic device includes a component that can be labeled as a “power supply” (like batteries in flashlights). However, it’s crucial to recognize that “power supply” typically implies converting existing electrical power into a form more suitable for a specific use. Often, these components are built into the device or circuit they power, though standalone units are also common.
One common example of a power supply is the electrical adaptation needed to power computers. Interestingly, this application often leads to more terminological confusion. A power supply unit (PSU) converts alternating current to direct current for a desktop computer, whereas a power brick is a specific type of standalone converter used for laptops. Despite their distinct functions, both terms are sometimes broadly used to refer to power supplies in general. Similarly, a power adapter technically refers to a component that enables a device to fit into a terminal with an otherwise incompatible shape. Yet, this term is also often used more generally to describe power supplies.
Power supplies are essential in the commercial sector, ensuring electric circuits operate within specific parameters. Without them, controlling electric circuits would be much more challenging, rendering them highly impractical.
There are a number of ways in which power supplies may be divided or categorized, including functionally, mechanically, and by power conversion method.
Parts
Every power supply is designed to efficiently channel electrical energy, featuring a power input to receive incoming energy and a power output to deliver the converted energy to the load. Typically, these inputs and outputs consist of hardwired circuit connectors or electrical connectors. Some power supplies, however, use wireless energy transfer instead of galvanic connections. The incoming electrical energy can originate from various sources, such as electrical transmission systems, solar power converters, fuel cells, batteries, generators, and alternators.
Despite the diversity among power supplies, many share common components. For instance, numerous computing power supplies include an input voltage switch, allowing them to adapt to different countries’ electrical outlets by adjusting the incoming external power.
Types
Power supplies can be categorized in several ways, typically based on their function, mechanical structure, or power conversion method, either individually or in combination.
Classifications by Conversion Methods
Given the definitions of power supply, conversion methods play a crucial role in their categorization. Power supplies are often described by their ability to convert incoming electric current into the appropriate output of current, voltage, or frequency.
Current is the precise rate at which electric charge moves.
Voltage represents the difference in electric charge between two distinct points in an electric circuit, acting as the driving force behind the flow of current.
Frequency denotes the count of cycles an electric circuit completes within a specified time frame.
At a broad level, power supplies are categorized into two types: linear and switching.
Linear power supplies handle input power directly, keeping all active conversion components within their linear operating regions. For instance, a frequency to voltage converter employs an operational amplifier to manage linear signals.
Switching power supplies dominate the power supply market. They convert input power into alternating current (AC) or direct current (DC) pulses before processing it. The conversion components in switching power supplies primarily function in non-linear regions, resulting in higher efficiency.
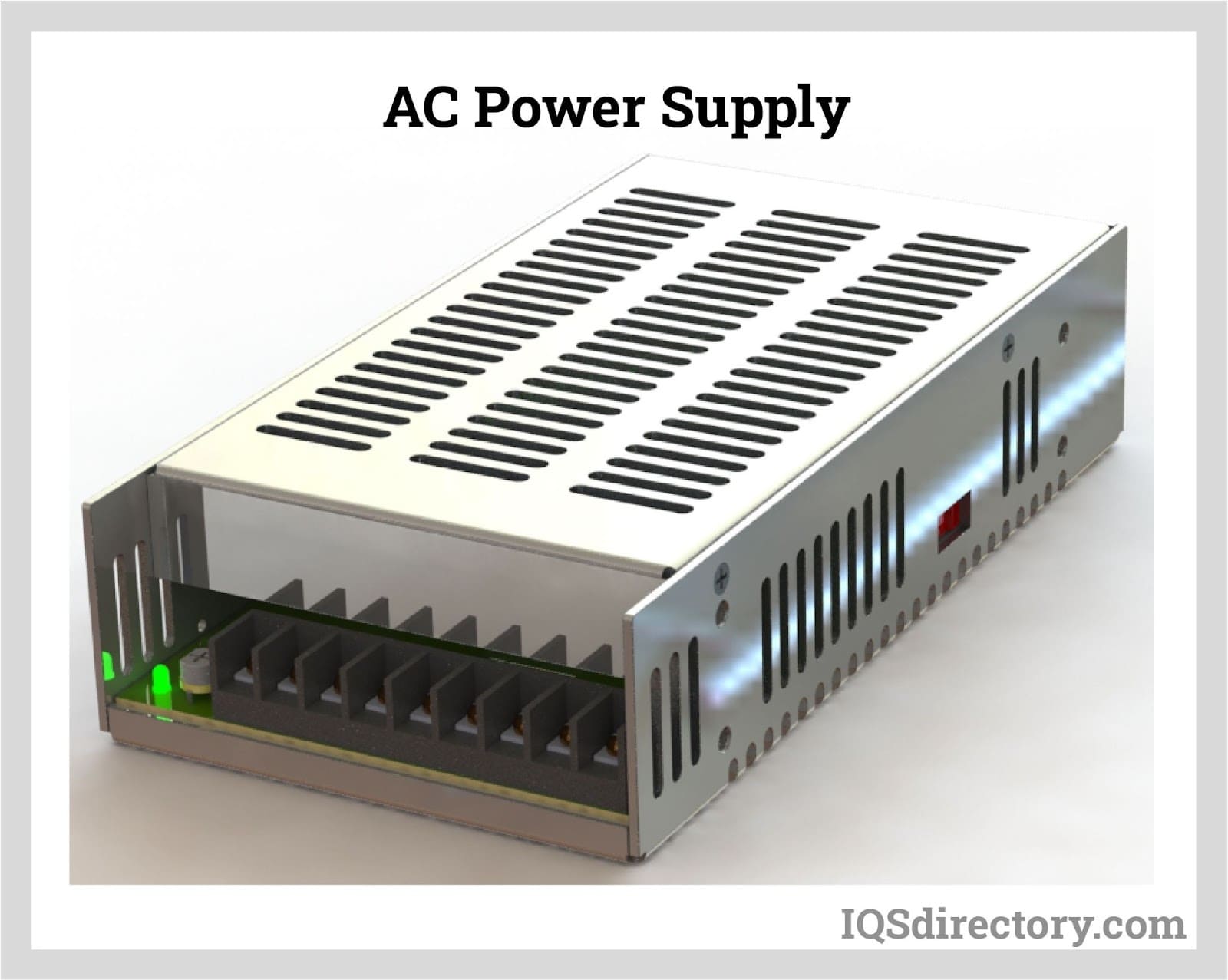
Most power supplies today are of the switching type, and a key distinction among them is whether they utilize alternating currents (AC) or direct currents (DC). The difference between AC and DC power is relatively simple. AC power supplies function through an electrical charge that periodically reverses direction at regular intervals. This reversal is measured in Hertz (Hz), with one Hertz equating to one cycle per second; for example, a 60 Hz current alternates sixty times in one second. Conversely, DC power supplies operate with an electrical charge that flows in a single, constant direction. Some power supplies can convert one type of current to another, such as an AC-DC power supply, or modify the current’s intensity.
Classification by Output
Functionally, power supplies may be divided into the following categories:
Regulated power supplies ensure a steady output, maintaining consistent current or voltage regardless of input fluctuations. They achieve this stability through the use of a voltage regulator alongside their output component. Some models incorporate multiple voltage regulators to support different outputs for various devices.
In contrast, unregulated power supplies deliver an output that fluctuates with changes in load current or input voltage. The output from these supplies can vary significantly, often adjusting by switching power sources on and off in response to voltage changes within the system. Consequently, these are also known as switched mode power supplies.
Adjustable power supplies stand out due to their ability to have programmable load currents or output voltages. These values can be adjusted using mechanical controls, a control input, or a combination of both. Compared to other types of power supplies, adjustable ones offer a broader range of variation and sophistication, capable of producing both AC and DC power.
Adjustable regulated power supplies create a hybrid category, encompassing power supplies that are both adjustable and regulated.
Isolated power supplies deliver power independently of their input source. Unlike typical power supplies, which share a common connector for both input and output, isolated power supplies keep these connections separate.
Classification by Structure
In terms of mechanics, power supplies may be classified according to the way they are packaged, or mechanically enclosed. Categories based on this methodology include the following:
Bench power supplies are independent desk units commonly employed in circuit testing and development.
Open frame power supplies are typically integrated directly into existing equipment or machinery, featuring only a partial mechanical enclosure. Sometimes, they consist merely of a mounting base.
Rack mount power supplies are designed to fit into standard electronic equipment racks.
Integrated power supplies are those that share a printed circuit board with their load.
Applications
A vast array of electronic devices relies either partially or entirely on various power supplies. Examples include computers, cell phones, battery chargers, kitchen appliances, industrial machinery, and electric motors. Certain power supplies are tailored to specific applications. For instance, frequency-to-voltage converters are frequently employed in automotive testing for evaluating tachometers and speedometers. Conversely, adjustable power supplies are commonly used in electron microscopes and scientific instruments for chemical analysis.
AC and DC power supplies serve distinct roles in powering various electrical devices. DC power supplies typically operate within metal conductors, medical equipment, process control systems, video technology, laptops, and cell phones. These power supplies are usually separate from the devices they power and are enclosed in protective casings. Conversely, AC power supplies are commonly used for electrical systems in residential and commercial buildings, as well as for electronic adapters or converters, owing to AC’s efficiency in long-distance transmission. Power supplies that convert AC to DC through electrical outlets and cords are among the most common types. Many household appliances that plug into AC outlets include a rectifier, made from diodes, to handle this AC to DC conversion. Conversely, some appliances operate by converting DC to AC, relying on inverters to transform DC into a smoothly varying, usable form of energy.
Considerations
Power supplies are available in numerous configurations and designs, offering customers various options for displaying monitored and measured current and voltage information. These options include analog visual indicators, graphic displays, video displays, and digital numerical displays. Additional features might include computer interface technology, adjustable voltage, fan cooling systems, water cooling, overvoltage protection, overcurrent protection, integral heat sinks, power factor correction, pure sine output, short circuit protection, and backup batteries. When choosing a power supply, it is also important to consider factors such as output voltage, output power, output frequency, number of outputs, apparent power, operating temperature, and whether the unit operates on direct current, alternating current, or both.
Investing time in choosing a reliable power supply provider is essential. Look for one that offers a wide selection of products and expert guidance to help you make the right choice. The following scenarios highlight some of the key factors to consider when selecting the best power supplies for your needs.
Switched mode power supplies excel in situations where maximizing energy efficiency is crucial. However, they are generally more intricate and generate more electrical noise compared to other types, such as linear power supplies. This interference sometimes necessitates extra shielding to prevent it from disrupting nearby electronic devices.
Unregulated power supplies typically cost less than regulated ones. However, as their name suggests, they do not provide stable or consistent power. Therefore, if you need to power sensitive electronic equipment, investing in regulated power supplies that deliver clean and reliable voltage is likely essential.
Choosing the Right Power Supply Manufacturer
To secure the ideal power supplies, choosing the right manufacturer is essential. The perfect partner will offer the customizations you need, the volume you require, and the certifications you desire. Moreover, they will provide high-quality products that fit within your budget and timelines. Check out our curated list of top manufacturers, featuring established industry leaders. Explore their offerings by visiting their websites through the provided links.








 Electric Coils
Electric Coils Electric Switches
Electric Switches Electric Transformers
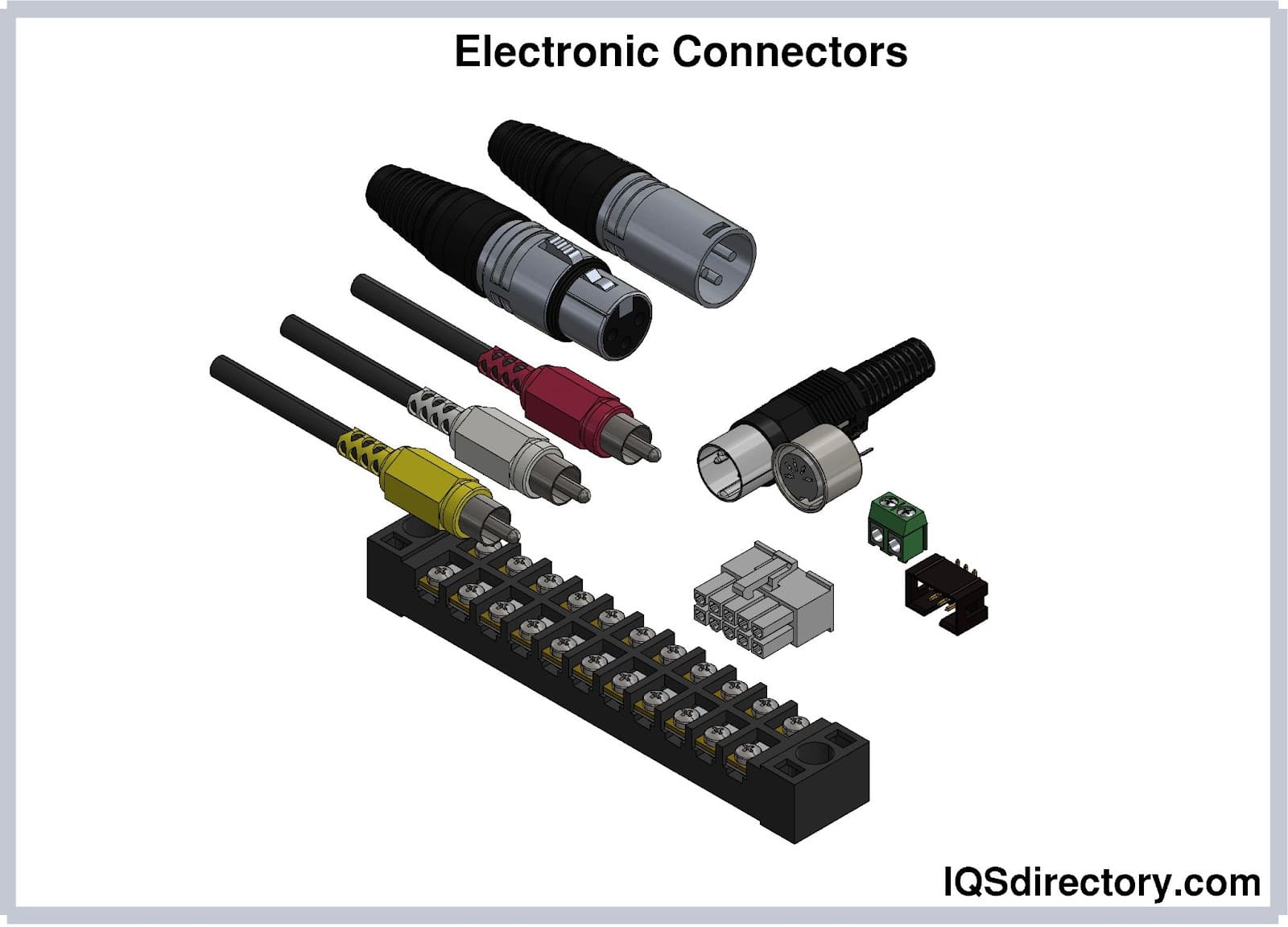
Electric Transformers Electronic Connectors
Electronic Connectors Electronic Enclosures
Electronic Enclosures Membrane Switches
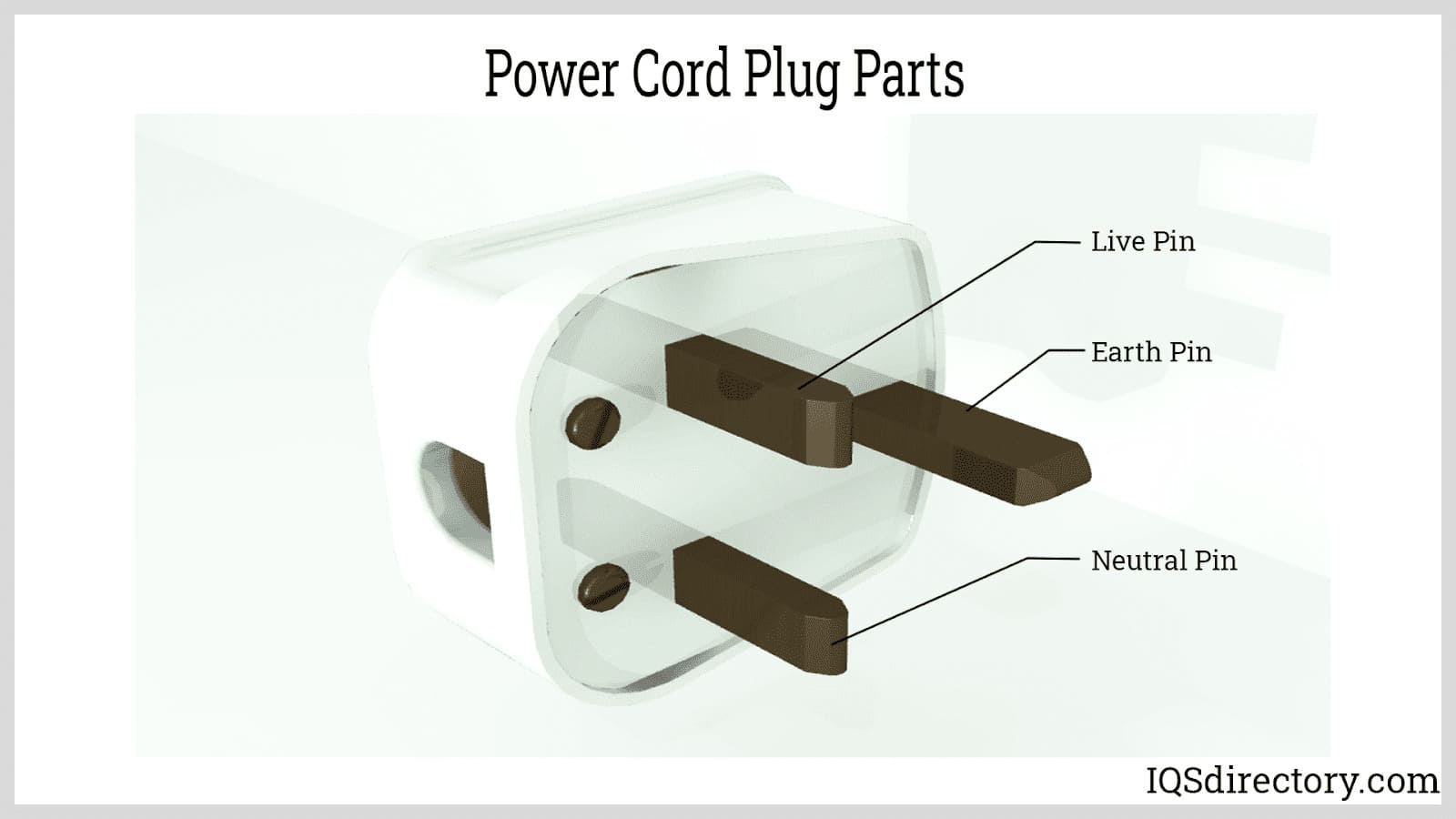
Membrane Switches Power Cords
Power Cords Power Supplies
Power Supplies Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services